Phishing is the fraudulent practice of sending emails or other messages purporting to be from reputable companies in order to induce individuals to reveal personal information, such as passwords and credit card numbers. This article highlights some major phishing types as a guide for reference.
Phishing scams are a type of social engineering attack that use fake emails or websites to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card numbers, and social security numbers. These scams often appear to come from legitimate organizations, such as banks or online retailers, and may contain urgent requests for personal information or threats to close accounts if information is not provided. To avoid falling victim to a phishing scam, it's important to never click on links in suspicious emails, verify the sender's email address, and never enter personal information on a website unless you are certain it is legitimate.
From a recent report, SlashNext's State of Phishing report reveals that there were 255 million phishing attacks in 2022, a 61% rise from the previous year. The attacks are getting more sophisticated. Recent examples show phishing emails are able to bypass Gmail's filter. The examples below might help prevent yourself from a few common phishing attacks patterns by raising awareness.
P.S. I have taken excerpts from various interesting blogs online mentioned in the reference section
The types of phishing include :
- Spear Phishing : Spear phishing involves targeting a specific group or individual, such as a company's system administrator. The following is an example of a spear phishing email. Observe the focus on the recipient's industry, the requested download link, and the urgent nature of the request.
- Whaling : Whaling is a highly targeted form of phishing that targets "the whales" - high-level executives within an industry or business, such as a CEO, CFO, or CXX. These attacks often claim that the company is facing legal trouble and require the recipient to click a link for further information.
- Vishing : Is similar in nature to other phishing attacks, with the goal of obtaining sensitive personal or corporate information. This type of attack is carried out through voice calls, hence the "v" in the name instead of "ph".
- Smishing : It is a type of attack that uses text messaging or SMS to deceive the target. A typical smishing tactic involves sending a message to a cell phone through SMS that contains a clickable link or return number.
- Email Phishing : The most prevalent form of phishing, has been in use since the 1990s. Attackers send these emails to any email addresses they can obtain, often claiming that there has been a breach to your account and requesting immediate action through a provided link. These attacks are often easy to identify due to spelling and grammar errors in the email. However, some phishing emails are harder to detect, especially when the language and grammar are polished. Checking the email's source and the linked website for suspicious language can provide clues as to its legitimacy
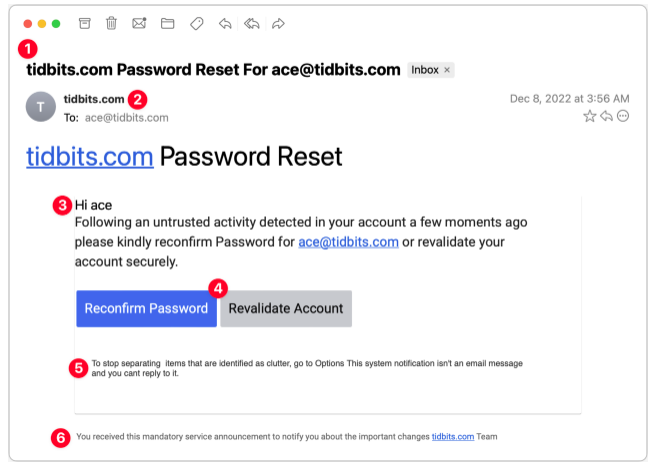
A.Password Reset
This phishing scam appears to originate from a system administrator responsible for my email domain and attempts to entice me into clicking a button. Although the text is poorly written, the buttons are well-designed, making it easy to imagine someone clicking without fully reading the text, especially if they are scanning quickly.
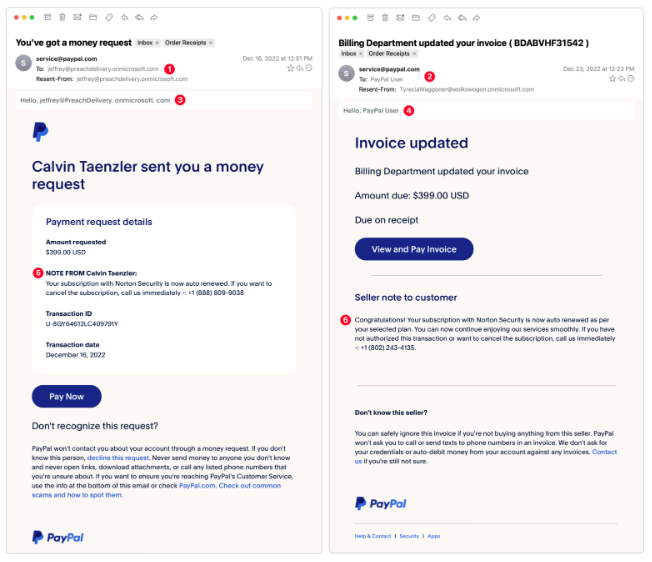
B.PayPal Money Request
These are exceptionally clever as they utilize authentic PayPal messages and include multiple anti-phishing warnings in the text. Despite this, there are still signs that give away their true nature. These messages arrived a week apart and are likely the result of a single phisher.
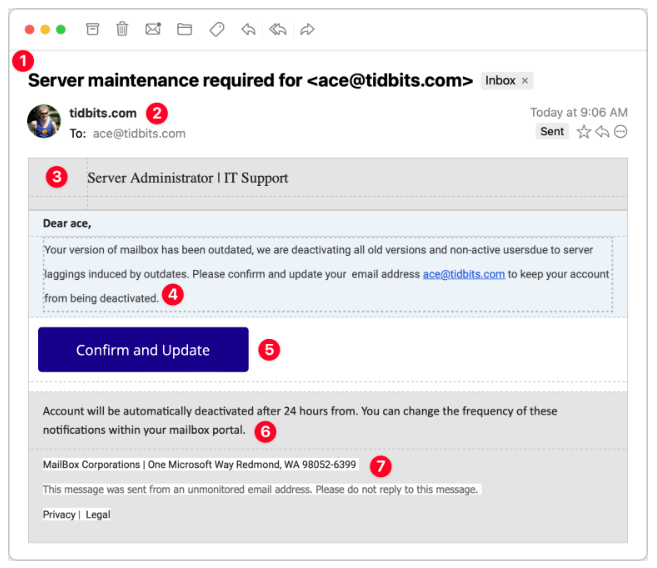
C.Server Maintenance
Consider this message claiming to be from my company's IT Support team. Its goal is to obtain your email password, as once an attacker gains control of your email, they can reset passwords on other sites and access sensitive accounts. It is crucial to safeguard your email password the most!
Some common patterns to be aloof of :
- Give emails a full read. Do not click if you have only skimmed through it. Be careful with easy emails and big buttons. Read the text carefully firsy before clicking. Look for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes in the email
- Verify with your IT department in person before honouring the claim on email
- An email with only an attached image and nothing else is mostly problem
- Be vary of the sender name and email addresses. Check for known ones.
An interesting question..can you mention the tell away signs in each phishing email example ? Comment below
Reference
- https://tidbits.com/2023/01/16/an-annotated-field-guide-to-identifying-phish/
- https://www.schneier.com/blog/archives/2023/01/a-guide-to-phishing-attacks.html
- https://cybersecurityguide.org/resources/phishing/
- https://www.valimail.com/guide-to-phishing/#:~:text=Most%20phishing%20attacks%20arrive%20via,tricking%20users%20into%20downloading%20malware.
- https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/what-is/phishing/types-of-phishing.html

Comments